C824 CAPSTONE TASK 1: HAND HYGIENE COMPLIANCE IN OPERATING ROOM
 Chapter 3: Implementation Steps: The implementation of hand hygiene protocol in the operating room (OR) involved a series of steps geared towards achieving effective hand hygiene compliance among staff.
Chapter 3: Implementation Steps: The implementation of hand hygiene protocol in the operating room (OR) involved a series of steps geared towards achieving effective hand hygiene compliance among staff.
Hand hygiene is a critical aspect of infection control in healthcare, especially in the OR where the risk of surgical infection is high. The initial step involved seeking approval from the hospital administration regarding the implementation of a new change in the organization. An initial draft explaining the importance of the new change was presented to the administrators.
The draft explained the various steps of implementing the change, including resources for pre- and post-implementation. The second step involved reviewing the WHO hand hygiene guidelines and identifying gaps among OR healthcare providers.
The hospital hand hygiene guidelines were reviewed with the help of the clinical nurse educator to ensure all aspects were included. The result was a complete guideline for hand hygiene that considered both the hospital policies and the WHO guidelines.

Struggling to meet your deadline?
Get your assignment on C824 CAPSTONE TASK 1: HAND HYGIENE COMPLIANCE IN OPERATING ROOM done by certified MDs and PhDs in the USA. ORDER NOW!
Steps to Implementing Hand Hygiene Protocol in the Operating Room
The implementation of hand hygiene compliance in the OR required the support from nurse leaders and staff. The third step involved sharing the new guidelines with the OR charge nurse and the clinical nurse educator. This step was necessary due to the power and influence of nurse leaders in achieving set goals. Upon approval of the whole plan by the administration and other leaders, the next step involved identifying key stakeholders and their roles during the implementation of the new change. The OR nurses were the primary stakeholders involved, alongside other healthcare providers like surgeons, surgical technicians, and subordinate staff. The intervention plan for hand hygiene compliance included the development of a multimodal plan that combined in-class education, hands-on simulation training, and professional modeling.
The Role of Nurse Leaders in Hand Hygiene Compliance
Nurse leaders play a significant role in hand hygiene compliance in the operating room. Their leadership ensures that the new protocols are understood, accepted, and implemented by the OR staff. These leaders are responsible for guiding the nursing staff through the changes and for ensuring that the education on best practices for handwashing in healthcare is effectively communicated.
Educational Strategies for Hand Hygiene Training
To ensure that OR staff acquired the necessary skills to wash their hands effectively, a comprehensive educational program was developed, using the WHO hand hygiene guidelines. Upon initial education, simulation training was provided to ensure proper hand hygiene techniques were learned. Demonstrations, such as the six steps for handwashing, were shown by the clinical nurse educator, with an emphasis on washing hands for 20 to 30 seconds. Additionally, professional modeling was emphasized during the implementation to ensure that nurse leaders were actively engaged in the process, leading by example.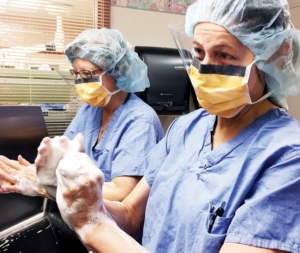
Overcoming Barriers to Hand Hygiene Implementation in the OR
Infection prevention and control in healthcare organizations, particularly in the operating room, continue to be a challenge despite the implementation of various changes. One barrier to hand hygiene compliance was the acceptance of the new change by the OR staff. Some argued that the new WHO hand hygiene guidelines were not much different from the CDC handwashing guidelines. Another barrier was the time constraints due to understaffing in the OR, which made it difficult to train staff properly.
The Importance of WHO Guidelines in Improving Hand Hygiene Compliance
The WHO hand hygiene guidelines played a pivotal role in shaping the new hand hygiene protocols in the operating room. These guidelines provided a systematic approach to infection control in hospitals, offering clear, evidence-based practices for improving surgical staff hand hygiene and patient safety in the operating room. The staff was educated on the significance of these guidelines and how they help in reducing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and improving HCAHPS scores.
Developing an Effective Multimodal Hand Hygiene Training Program
The development of a multimodal education program for hand hygiene compliance was critical. This program included in-class education, hands-on simulation training, and professional modeling. The combination of these methods helped ensure that OR staff understood the importance of infection prevention education for nurses and were equipped to apply hand hygiene best practices in the operating room.
Impact of Hand Hygiene Compliance on Patient Safety
Hand hygiene compliance directly impacts patient safety in the operating room. Proper hand hygiene helps reduce surgical infection rates and healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). By implementing WHO hand hygiene guidelines, the risk of surgical infections is minimized, contributing to better patient outcomes and overall healthcare quality.
Adapting Education for Day and Night Shift OR Staff
Given the busy nature of the OR and the different shifts, adapting education for both day and night shift staff was crucial. Due to the time constraints and understaffing, the education program was split to accommodate all staff, ensuring that both day and night shifts received the necessary training on hand hygiene. The clinical nurse educator also incorporated online education programs for nurses to provide additional support and ensure all staff were adequately trained.
Using Online Education to Enhance Hand Hygiene Compliance
To enhance hand hygiene compliance, online education programs for nurses were used. These programs included videos and resources that helped staff members reinforce their hand hygiene skills, ensuring that both day and night shift staff could access the training materials at their convenience. This online education helped bridge the gap in training availability and ensured consistent education across shifts.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Hand Hygiene Implementation Plan
The success of the hand hygiene implementation plan was evaluated through monitoring compliance and feedback from OR staff. During the four-week monitoring period, staff were observed and assessed on their adherence to the new hand hygiene protocols. The clinical nurse educator and nurse leaders played a key role in assessing the effectiveness of the training and making necessary adjustments to the plan.
Challenges in Educating Staff on Hand Hygiene Guidelines
Despite the comprehensive education program, some challenges persisted in educating staff about the new hand hygiene guidelines. One challenge was staff resistance to the perceived difference between CDC and WHO hand hygiene guidelines. This resistance was addressed through education and discussion, emphasizing the importance of hand hygiene and its role in reducing infections in the OR.
Strategies to Overcome Staff Resistance to New Hand Hygiene Guidelines
To overcome staff resistance to the new WHO guidelines, a thorough education program was used. Staff were educated on the differences between CDC and WHO guidelines, particularly the recommended duration for handwashing (20 to 30 seconds). This education helped the staff understand the importance of these practices in reducing healthcare-associated infections and improving patient safety.
Conclusion: Sustaining Hand Hygiene Compliance in the Operating Room
To sustain hand hygiene compliance in the operating room, continuous education and reinforcement are necessary. By involving nurse leaders, using multimodal education strategies, and addressing barriers such as understaffing and resistance, the hospital can ensure long-term success in maintaining hand hygiene protocols. Furthermore, online education programs and regular monitoring will continue to play a key role in promoting infection control in healthcare settings.
Identification of Interprofessional Relationships
Nursing’s Role in Interprofessional Collaboration
In healthcare, interprofessional collaboration is critical for providing high-quality care to patients and for fostering a positive work environment among healthcare providers. Nurses play a significant role in this collaboration, as they often serve as the main point of contact for patients and are involved in all aspects of patient care. Interprofessional collaboration in nursing practice involves working with other healthcare professionals such as physicians, surgeons, therapists, and clinical nurse educators. These collaborations are crucial when implementing evidence-based practices like infection prevention, surgical nursing, and improving healthcare outcomes. Nurses are often at the forefront of patient safety initiatives, making them integral in guiding change and ensuring that evidence-based practices, such as the implementation of infection control measures, are followed effectively.
The role of nurses in interprofessional collaboration cannot be overstated. They facilitate communication among team members, ensuring that all perspectives are considered when making decisions that impact patient care. By working closely with other professionals in healthcare teams, nurses contribute significantly to improving clinical outcomes. In the context of healthcare quality improvement, nurses, together with surgeons and other staff, collaborate to reduce the risk of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) by adhering to strict infection control measures. This collaboration fosters a unified approach to quality improvement in healthcare and helps achieve better clinical outcomes for patients.
Interprofessional Collaboration in Healthcare Change
Interprofessional collaboration is particularly crucial when implementing healthcare changes. One such area of change involves infection prevention practices, including the implementation of WHO guidelines for hand hygiene. Nurses, surgeons, surgical technicians, and clinical nurse educators all contribute to the successful execution of these protocols. By working together, they ensure that each healthcare provider understands their role in preventing infections and improving patient safety. Collaboration in these contexts ensures that evidence-based nursing practices are followed, reducing the likelihood of complications, such as infections during surgical procedures.
Healthcare professionals involved in interprofessional collaboration also help each other overcome resistance to change. Resistance to change in healthcare settings is common due to various factors, including existing habits, lack of awareness, and reluctance to adopt new protocols. However, with effective leadership and open communication, resistance can be overcome, allowing the implementation of more effective infection prevention measures.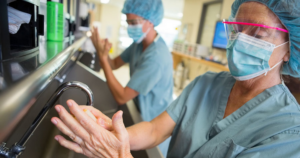
Understanding the Importance of Hand Hygiene in Healthcare
Hand hygiene is one of the most effective methods for preventing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). For healthcare professionals, it is vital to follow established hand hygiene protocols to reduce the risk of transmitting infections to patients. The WHO has established comprehensive hand hygiene guidelines that provide clear instructions for healthcare workers on how to properly wash their hands to prevent the spread of infections. Nurses, as key members of the healthcare team, play a central role in educating other healthcare workers about these guidelines and ensuring compliance within their departments.
The implementation of hand hygiene protocols in healthcare settings is critical for improving patient safety and reducing the spread of infections. Studies have shown that proper hand hygiene can significantly lower the incidence of surgical infections, which directly impacts clinical outcomes and patient recovery. Nurses are instrumental in advocating for and ensuring adherence to these protocols, and their leadership is essential for sustaining high levels of compliance across the healthcare team.
Evidence-Based Nursing Practices for Infection Prevention
Infection prevention is a cornerstone of nursing practice, particularly in surgical nursing. Evidence-based nursing practices focus on the use of current research and clinical evidence to guide decision-making and improve patient care. In surgical settings, this means following established infection control measures and ensuring that every member of the healthcare team adheres to evidence-based guidelines, such as those for hand hygiene, to prevent the spread of infections.
Nurses, in particular, play an important role in implementing these evidence-based practices. They are often responsible for monitoring infection control measures and ensuring that surgical teams comply with infection prevention protocols. By following evidence-based practices, nurses help reduce the incidence of HAIs, improve surgical outcomes, and contribute to overall healthcare quality improvement. Adhering to infection prevention strategies based on evidence ensures that patients receive the best possible care while minimizing their risk of complications.
Improving Healthcare Outcomes Through Quality Improvement
Quality improvement in healthcare is an ongoing process that seeks to improve patient care, enhance safety, and ensure that healthcare services are efficient and effective. One of the most important aspects of quality improvement is the implementation of evidence-based practices that have been shown to reduce complications and improve patient outcomes. In the context of nursing, this involves adhering to infection prevention protocols and ensuring that all healthcare professionals are properly trained in these practices.
Quality improvement initiatives often focus on reducing the rates of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) through strategies such as improved hand hygiene practices, better patient education, and enhanced collaboration among healthcare providers. Nurses are central to these initiatives, as they are responsible for ensuring that infection control measures are followed and for identifying areas where improvements can be made. By continually evaluating and refining infection prevention strategies, nurses help drive improvements in healthcare quality and patient safety.
Challenges in Implementing Evidence-Based Hand Hygiene Guidelines
Despite the established benefits of hand hygiene for infection prevention, healthcare settings often face challenges in implementing and maintaining these practices. One of the main challenges is the resistance from healthcare workers, who may be reluctant to change their habits or may not fully understand the importance of following hand hygiene protocols. To overcome this resistance, it is crucial to provide ongoing education and training for healthcare workers, especially nurses, who play a significant role in monitoring and enforcing hand hygiene guidelines.
The implementation of the WHO guidelines for hand hygiene in healthcare settings can also be hampered by resource limitations, such as a lack of sufficient handwashing stations, soap, and sanitizers. Nurses must work closely with hospital administrators to ensure that the necessary resources are available and that staff are trained on how to use them properly. Regular audits, feedback, and the involvement of nurse leaders in advocating for hand hygiene compliance are essential for overcoming these challenges.
Barriers to Healthcare Change and How to Overcome Them
Barriers to healthcare change, such as those encountered during the implementation of infection prevention protocols, can arise due to various factors. These may include resistance to new practices, lack of resources, insufficient training, and time constraints. Overcoming these barriers requires a strategic approach that includes education, leadership, and clear communication.
One effective way to overcome resistance to healthcare change is to engage healthcare providers early in the process, allowing them to express concerns and participate in discussions about how to implement new practices. Providing evidence of the benefits of the proposed changes, such as the reduction of HAIs through improved hand hygiene, can also help reduce resistance. Nurse leaders can help overcome barriers by championing the change process and encouraging their colleagues to embrace evidence-based practices for infection prevention and patient safety.
Effective Nurse Leadership in Promoting Healthcare Change
Nurse leadership is crucial for driving change in healthcare settings. Nurse leaders are responsible for guiding their teams through the change process, ensuring that staff are educated on new practices, and holding them accountable for adhering to established protocols. Effective leadership can help overcome resistance to change and create a culture of safety and quality improvement within healthcare organizations.
Nurse leaders play a key role in promoting the adoption of evidence-based practices, such as the implementation of hand hygiene guidelines. By modeling proper hand hygiene and reinforcing its importance, nurse leaders set an example for their teams and encourage compliance with infection prevention protocols. Their leadership also ensures that any barriers to change, such as resource limitations or time constraints, are addressed in a timely manner.
The Role of Clinical Nurse Educators in Implementing Change
Clinical nurse educators play an essential role in implementing healthcare changes, particularly in areas related to infection prevention and quality improvement. Nurse educators are responsible for designing and delivering educational programs that teach healthcare workers about new practices and ensure that they have the skills necessary to implement them effectively. In the case of hand hygiene, nurse educators work closely with OR staff, including nurses, surgeons, and surgical technicians, to ensure they understand and follow the WHO guidelines for proper handwashing.
Nurse educators also help bridge the gap between theory and practice by offering hands-on simulation training, providing role models, and facilitating ongoing education for healthcare workers. Their expertise in training and education ensures that healthcare teams are well-prepared to adopt evidence-based practices and that any challenges encountered during the implementation phase are addressed promptly.
Surgical Nursing and Infection Control Measures
In surgical nursing, infection prevention is a top priority. Nurses are responsible for ensuring that infection control measures are followed before, during, and after surgery. These measures include proper hand hygiene, sterile techniques, and the use of protective equipment. Surgical nurses also monitor patients for signs of infection and work closely with surgeons and other healthcare professionals to manage and prevent any potential complications.
The implementation of infection prevention protocols, such as the WHO guidelines for hand hygiene, is essential for reducing the risk of surgical infections. By adhering to these guidelines, surgical nurses play a crucial role in improving patient safety and surgical outcomes. Infection control measures in surgical settings are vital for maintaining healthcare quality and ensuring that patients recover without complications.
Patient Safety and the Role of Nurses in Infection Prevention
Nurses are the frontline caregivers in healthcare settings and are directly involved in patient safety. One of the most important ways nurses ensure patient safety is by adhering to infection prevention protocols. Hand hygiene is a fundamental part of these protocols and plays a critical role in preventing the spread of infections in healthcare settings. Nurses are responsible for monitoring the implementation of hand hygiene practices, educating patients and staff about their importance, and ensuring that healthcare providers follow the appropriate procedures to reduce the risk of infections.
By prioritizing patient safety and focusing on infection prevention, nurses contribute significantly to improving healthcare outcomes. They ensure that patients receive the highest standard of care while minimizing the risk of complications such as infections. Nurses also play a key role in advocating for patient safety initiatives and leading efforts to improve the quality of care provided.
Improved Compliance with WHO Hand Hygiene Guidelines
One of the most notable successes in healthcare settings is improved compliance with hand hygiene guidelines, particularly those set forth by the World Health Organization (WHO). The WHO guidelines have been shown to be highly effective in preventing the spread of infections, including hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), which are a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in healthcare facilities. Nurses, working closely with surgeons and other healthcare providers, have been instrumental in promoting and ensuring compliance with these guidelines.
By educating staff about the importance of hand hygiene and modeling proper practices, nurses have helped improve compliance with WHO guidelines across healthcare settings. This, in turn, has led to a decrease in the rate of HAIs, improved patient outcomes, and enhanced patient safety. The continued promotion of WHO guidelines for hand hygiene is a key aspect of quality improvement in healthcare and a critical component of nursing practice.
Best Practices in Surgical Infection Prevention
In surgical settings, infection prevention is paramount. Best practices for preventing surgical infections include strict adherence to hand hygiene protocols, maintaining a sterile environment, and following evidence-based guidelines for patient care. Nurses play a central role in implementing these best practices by ensuring that surgical teams follow infection control measures and by monitoring patients for signs of infection.
Incorporating evidence-based practices, such as the WHO guidelines for hand hygiene, into surgical infection prevention protocols is crucial for reducing the incidence of infections and improving patient outcomes. Nurses collaborate with surgeons and other healthcare professionals to ensure that these practices are followed, contributing to the overall success of surgical procedures and enhancing patient safety.
Collaborative Approaches to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
Hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) are a significant concern in healthcare settings, particularly in surgical units. Reducing the risk of HAIs requires a collaborative approach that involves all members of the healthcare team. Nurses, surgeons, surgical technicians, and clinical educators must work together to ensure that infection control measures, such as proper hand hygiene, are consistently followed.
Collaborative efforts to reduce HAIs involve ongoing education, regular audits, and feedback to ensure that infection prevention protocols are being followed correctly. Nurses are often at the forefront of these efforts, monitoring compliance with hand hygiene guidelines, providing education to staff, and advocating for necessary changes to improve infection control practices.
Training and Education for Improving Hand Hygiene Compliance
Training and education are essential for improving hand hygiene compliance in healthcare settings. Nurses, as educators and role models, play a critical role in ensuring that healthcare workers understand the importance of hand hygiene and are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to adhere to established protocols. Ongoing education and training sessions help reinforce the importance of proper hand hygiene and ensure that healthcare workers are prepared to implement best practices consistently.
In addition to formal education programs, simulation training and hands-on practice can enhance the understanding and application of hand hygiene protocols. Nurses play a central role in delivering this training and ensuring that healthcare teams are well-prepared to reduce the spread of infections and improve patient safety.
Post-Implementation Support for Healthcare Change Initiatives
The successful implementation of healthcare changes, such as the adoption of WHO hand hygiene guidelines, requires ongoing support and monitoring. After the initial education and training phases, healthcare organizations must provide continuous support to ensure that changes are sustained and that staff remain committed to best practices.
Post-implementation support includes regular audits, feedback sessions, and the provision of resources to help healthcare providers adhere to new practices. Nurse leaders and educators play a vital role in providing this support, ensuring that healthcare teams continue to prioritize infection prevention and patient safety long after the initial implementation phase.
Sustaining Healthcare Improvements: Policies and Practices
Sustaining improvements in healthcare quality requires the establishment of policies and practices that reinforce best practices and ensure long-term success. Policies that mandate adherence to hand hygiene protocols and provide guidelines for infection control are essential for sustaining improvements in patient safety and healthcare outcomes.
Nurse leaders should work with administrators to develop policies that support ongoing education, provide necessary resources, and hold healthcare workers accountable for their practices. By reinforcing these policies and creating a culture of continuous improvement, healthcare organizations can sustain the positive changes made in infection prevention and other areas of patient care.
Key Components of Successful Quality Improvement Projects in Healthcare
Successful quality improvement projects in healthcare require several key components: evidence-based practices, interprofessional collaboration, leadership, education, and ongoing monitoring. In the case of infection prevention, using evidence-based guidelines, such as the WHO hand hygiene protocols, is crucial for achieving positive outcomes.
Interprofessional collaboration is also essential for ensuring that all healthcare providers are aligned in their goals and practices. Nurse leaders, in particular, play a critical role in guiding and motivating their teams, ensuring that quality improvement initiatives are successfully implemented and sustained.
The Importance of Simulation Training for Healthcare Professionals
Simulation training is an essential tool for improving healthcare professionals’ skills and understanding of infection prevention practices. By providing hands-on experience in a controlled environment, simulation training allows healthcare workers to practice and refine their skills, ensuring that they are prepared to handle real-life scenarios effectively. Nurses, as educators, can incorporate simulation training into their educational programs to help staff understand and apply infection prevention protocols.
Enhancing Patient Outcomes Through Collaborative Healthcare Teams
Collaborative healthcare teams are key to enhancing patient outcomes. Nurses, along with other healthcare professionals, work together to ensure that patients receive comprehensive, high-quality care. In surgical settings, this collaboration is essential for preventing infections and ensuring that surgical procedures are carried out safely and effectively.
By working together and implementing evidence-based practices such as hand hygiene, healthcare teams can improve patient outcomes, reduce complications, and contribute to overall healthcare quality improvement. Nurses are central to this collaboration, ensuring that infection prevention protocols are followed and that patient safety remains a top priority.
References
World Health Organization. (2009). WHO guidelines on hand hygiene in health care: first global patient safety challenge clean care is safer care [eBook]. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/gpsc/5may/tools/who_guidelines-handhygiene_summary.pdf

Dont wait until the last minute.
Provide your requirements and let our native nursing writers deliver your assignments ASAP.